
#How to use tor search engine software#
Tor software operating on a Tor host will create a local file directory, assign a port number for the service, and generate a public-private key pair when it configures a hidden service. Dark Web users often find names out of band, for example, from pastebin or Dark Web market lists. Any computer that runs Tor software can host a hidden (e.g., web) service. These are always 16-character values prepended to the. Unlike the human-readable domain names that we are accustomed to using when we navigate the web, Dark Websites use names of Tor hidden services.
All connections are short-lived to prevent observation of behavior over time.Ĭonstructed using these properties, these Tor private network pathways defeat traffic analysis and support the ability to publish content without revealing identity or location.Each connection between relays is uniquely encrypted.No relay point knows the entire path between circuit endpoints.Tor circuits have three important properties. Instead, Tor clients create circuits through relay points in the Tor network.

Like VPNs, Tor networks use virtual tunnels, but unlike VPNs, these tunnels don't connect clients directly to servers. Tor serves many good purposes, but also attracts Dark Web users wanting to keep their activities or marketplaces secret and untraceable. Who uses Tor? Journalists, whistleblowers, dissidents, or generally any Internet users who do not want third parties to track their behavior or interests. Tor networks are popular solutions for maintaining anonymity and privacy and for defeating traffic analysis. Traffic analysis is related to metadata collection, a topic we've covered in an earlier post. Conventional routing, however, is susceptible to traffic analysis, a surveillance technique that can reveal traffic origins, destinations and times of transmission to third parties. VPN connections typically abide by the conventional behavior of Internet routing for (1) the determination of an end-to-end path from a user's computer to a server that hosts content that the user wants to access, and (2) the bidirectional transmission of requests and response traffic along this path. Many Internet users use encryption – for example, Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) – to keep Internet activities private. Leave No Trace: Encryption and Evasion for the Dark Web
#How to use tor search engine how to#
Novices can even purchase eBooks that explain how to attack websites, steal identities or otherwise profit from illegal activities.īut you can also use the Deep Web to anonymously share information with media outlets such as the New York Times, the Washington Post, The Intercept and others, as well use search engines without giving up your privacy, or engage in legitimate e-commerce network such as OpenBazaar. You can contract digital or criminal services, ranging from spam campaigns to distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks. You can buy or broker illegal drugs, weapons, counterfeit goods, stolen credit cards or breached data, digital currencies, malware, national identity cards or passports. Some Deep Websites are unconventional marketplaces that offer a disturbing range of products or services. The Deep Web is the collection of all websites that are not indexed by search engines.
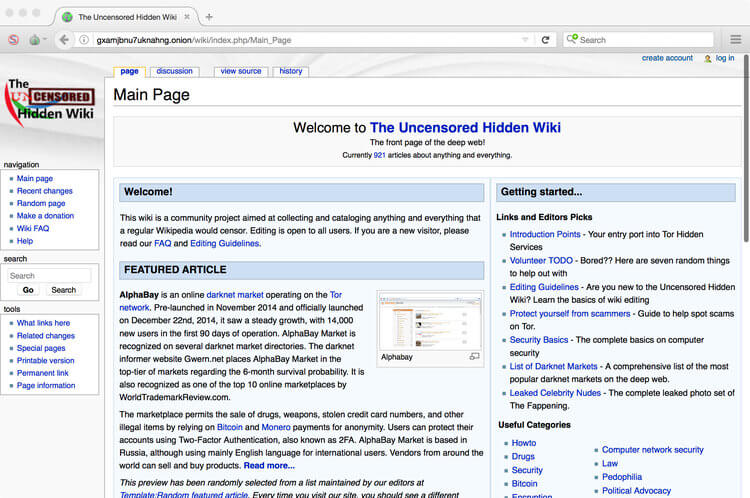
Many users use Tor and similar services as a means to provide freedom of expression and association, access to information, and the right to privacy. The Dark Web is only accessible through services such as Tor. It allows for the publication of websites and the dissemination of information without revealing the publisher's identity or location. The Dark Web is an important part of the Internet ecosystem. This is the Dark Web, a land of hidden services, where leaving no tracks and preserving anonymity are valued over search engine rankings and web experience personalization. There is another part of the Web, however, where publishers and visitors want to navigate websites and conduct business transactions in secret. The publishers of these billion websites compete for search engine relevance and the attention of nearly 3.6 billion Internet users.
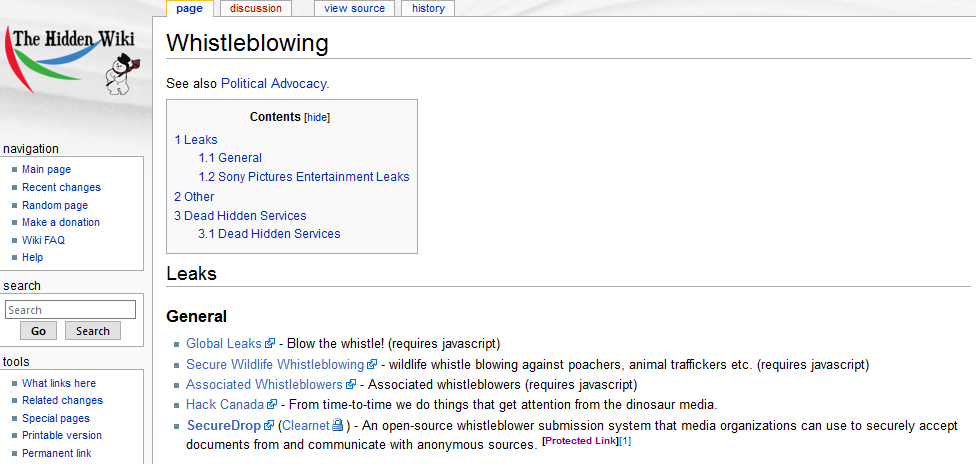
According to Internet Live Stats, the World Wide Web passed the one billion website benchmark in 2014 and is still hovering around that figure.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
